If you are involved in website hosting or network administration, you have likely come across the term ‘fully qualified domain name’or FQDN. But what exactly does this term mean and why is it important?
In this article, we will explain the concept of FQDN in detail, including how it works and why it is crucial for correct network communication.
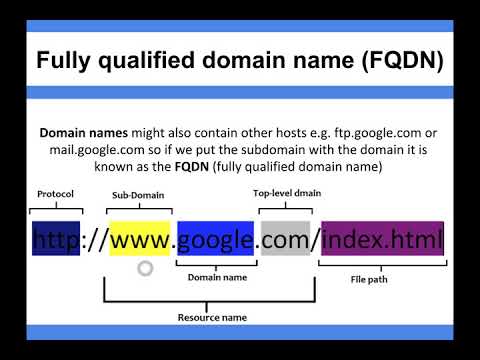
At its most basic level, an FQDN is a domain name that includes the complete hierarchy of domain labels, from the top-level domain to the hostname. This means that it includes not only the domain name itself (such as example.com), but also the subdomains (such as www.example.com) and any additional labels that identify a specific host within that subdomain (such as mail.www.example.com).
Related Video: "Networking - Fully qualified domain names (FQDN)" by TeachingCS
By providing this full and specific address, an FQDN allows for precise identification and communication within a network, making it an essential tool for website hosting, email delivery, and other network functions.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
– FQDN is a domain name with complete hierarchy of labels, specifying a host’s exact location within the DNS hierarchy.
– FQDN is crucial for network communication and security, and is used for email routing, website hosting, and network administration.
– ACLs and email servers use FQDN to manage access permissions and identify sender’s domain, respectively.
– Proper FQDN maintenance, including unique and descriptive names, up-to-date FQDNs, limited access, and monitoring for unauthorized changes, reduces risk of network downtime and unauthorized access.
Definition of FQDN
So, you’re probably wondering what an FQDN is, right? Well, let me break it down for you.
An FQDN, or fully qualified domain name, is a domain name that specifies a host’s exact location within the DNS hierarchy. It consists of several parts, including the host name, domain name, and top-level domain (TLD), all separated by periods.
The importance of FQDNs lies in their ability to uniquely identify a specific location on the internet. They were first introduced in the early days of the internet as a way to organize and manage the growing number of websites.
Today, FQDNs are used for a variety of purposes, including email routing, website hosting, and network administration.
Now that you understand what an FQDN is and its history, let’s dive into how it works.
How FQDN Works
You’re probably wondering how FQDN functions, and it’s like a roadmap that leads you to your destination, with each part of the address providing crucial information to get you there.
FQDN is comprised of several parts, including the hostname, domain name, and top-level domain. When you enter a FQDN into your web browser, your computer begins the process of DNS resolution to locate the IP address associated with that domain name.
The domain hierarchy plays a crucial role in FQDN functionality. The domain hierarchy is a system that organizes domain names into a tree-like structure, with each level representing a different section of the domain name. This hierarchy allows for easy navigation and organization of domain names.
FQDN works by following the domain hierarchy, starting at the root domain, and navigating through each level until it reaches the specific domain name requested. DNS resolution then maps the FQDN to an IP address, allowing you to access the desired website. This process is essential for the functioning of the internet as we know it, and highlights the importance of FQDN in modern technology.
Moving onto the next topic, the importance of FQDN lies in its ability to provide a unique and identifiable address for every device on the internet.
Importance of FQDN
The significance of FQDN lies in its ability to assign a unique and recognizable identity to every device connected to the internet. This is important for security implications, as FQDN allows for more precise identification and tracking of devices on a network. In addition, FQDN enables efficient DNS resolution performance, as it provides a more specific and accurate domain name for the DNS server to locate.
To better understand the importance of FQDN, consider the following table:
| FQDN | IP Address |
|---|---|
| —- | ———- |
| www.example.com | 192.0.2.1 |
| mail.example.com | 192.0.2.2 |
| ftp.example.com | 192.0.2.3 |
| api.example.com | 192.0.2.4 |
| db.example.com | 192.0.2.5 |
In this table, each FQDN is assigned a unique IP address, allowing for precise identification and communication between devices on the network. This not only improves security, but also enhances DNS resolution performance by providing a more specific domain name for the DNS server to locate.
The importance of FQDN cannot be understated, as it provides a critical foundation for network communication and security. With a better understanding of FQDN and its significance, we can now move on to practical examples of FQDN in action.
Practical Examples of FQDN
Get ready to see FQDN in action as we explore practical examples that showcase its importance in network communication and security. FQDN provides a unique identification for devices connected to a network, and this makes it an essential tool in managing and securing network traffic.
One practical example of FQDN use case is in access control lists (ACLs). ACLs are a set of rules that define which devices or users have permission to access specific resources on a network. By using FQDN in ACLs, network administrators can easily manage access permissions without having to manually update the list every time a device is added or removed from the network.
Another example of FQDN use case is in email communication. Email servers use FQDN to identify the sender’s domain, which helps in filtering out spam and ensuring that emails are sent from legitimate sources. FQDN also plays a critical role in web server management. For instance, when a user enters a URL in a web browser, the browser uses FQDN to identify the web server that hosts the requested web page. This helps in ensuring that the user is directed to the correct web page, and it also helps in load balancing across multiple servers.
As you can see, FQDN is a crucial tool in network communication and security. However, managing FQDN can be challenging, and that’s why it’s essential to follow best practices for FQDN management.
Best Practices for FQDN Management
Maximize the security and efficiency of your network by implementing best practices for managing FQDNs. Proper FQDN maintenance is crucial for a smooth and secure network operation. Here are some guidelines that can improve the management of your FQDNs:
– Use unique and descriptive names: Ensure that your FQDNs are unique and describe the purpose of the associated resource. This will prevent confusion and help you quickly identify and troubleshoot issues.
– Keep FQDNs up-to-date: Regularly review your FQDNs to ensure they reflect the current state of your network. This includes removing outdated entries and updating IP addresses for hosts that have moved.
– Limit access to FQDN management: FQDNs are an essential part of your network infrastructure and should be treated as such. Limit access to FQDN management to only authorized personnel to prevent unauthorized changes that can compromise your network security.
– Monitor for unauthorized changes: Regularly monitor your FQDNs for any unauthorized changes that can indicate a security breach. Implement a log system that tracks all changes made to FQDN entries, and set up alerts to notify you of any unexpected modifications.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your FQDNs are correctly maintained and secured, reducing the risk of network downtime and unauthorized access. Remember to always prioritize network security and continuously review your FQDNs to keep them up-to-date.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a FQDN and a hostname?
A hostname is a single word identifying a device, while an FQDN includes the hostname plus domain name. FQDN syntax rules dictate the order of the components. FQDNs are used for more precise network communication.
Can a FQDN contain special characters or spaces?
Hey there! You can’t use special characters or spaces in a FQDN. Best practices for FQDN naming conventions suggest sticking to alphanumeric characters and hyphens. Keep it simple and precise!
How do I check if a FQDN is valid?
To check FQDN validity, ensure it adheres to FQDN syntax rules. It must include a hostname and domain name separated by a dot, with no spaces or special characters. Use a DNS lookup tool for verification.
Are there any security risks associated with using FQDNs?
Mitigating FQDN security risks is crucial for network administrators. Best practices include ensuring that all FQDNs are properly registered and using SSL certificates for secure communication. Failure to do so can result in phishing attacks and data breaches.
Can a FQDN be changed after it has been set up?
Changing your FQDN after setup can cause a domino effect on your DNS records. You’ll need to update every record that references the old FQDN, which can be a tedious and time-consuming process.



